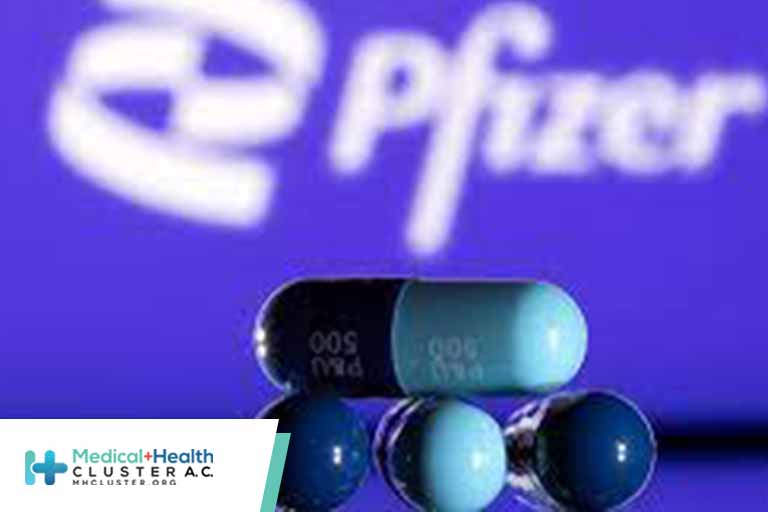
Pfizer Inc on Tuesday said final analysis of its antiviral COVID-19 pill still showed near 90% efficacy in preventing hospitalizations and deaths in high-risk patients, and recent lab data suggests the drug retains its effectiveness against the fast spreading Omicron variant of the coronavirus.
The U.S. drugmaker last month said the oral medicine was around 89% effective in preventing hospitalizations or deaths when compared to placebo, based on interim results in around 1,200 people. The data disclosed on Tuesday includes an additional 1,000 people.
Nobody in the trial who received the Pfizer treatment died, compared with 12 deaths among placebo recipients.
The Pfizer pills are taken with the older antiviral ritonavir every 12 hours for five days beginning shortly after onset of symptoms. If authorized, the treatment will be sold as Paxlovid.
“It’s a stunning outcome,” Pfizer Chief Scientific Officer Mikael Dolsten said in an interview.
“We’re talking about a staggering number of lives saved and hospitalizations prevented. And of course, if you deploy this quickly after infection, we are likely to reduce transmission dramatically,” Dolsten said.
Pfizer also released early data from a second clinical trial suggesting that the treatment reduced hospitalizations by around 70% in a smaller trial of standard-risk adults, including some higher-risk vaccinated people. The results were not statistically significant, but Pfizer said they showed a “positive data trend for reduction in risk.”
The trial did not show that the drug alleviated symptoms of COVID-19 in the same population.
Dolsten said he expects authorization for use in high-risk individuals from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and other regulatory agencies soon. He does not believe an FDA advisory panel meeting will be needed.
“We’re in very advanced regulatory dialogues with both Europe and the UK, and we have dialogues with most of the major regulatory agencies globally,” Dolsten said.
‘VERY EXCITING RESULTS’
Pfizer submitted data to the U.S. FDA last month, asking for emergency use authorization of the drug.
“These are very exciting results,” said Dr. Paul Sax, a professor at Harvard Medical School.
Sax said the FDA should try to accelerate the authorization process as much as possible, noting there are very limited treatment options for high-risk people outside of the hospital.
There are currently no oral antiviral treatments for COVID-9 authorized in the United States.
Analysts on average forecast 2022 revenue of more than $24 billion from the pill, which would more than make up for any decline in vaccine sales after 2021.